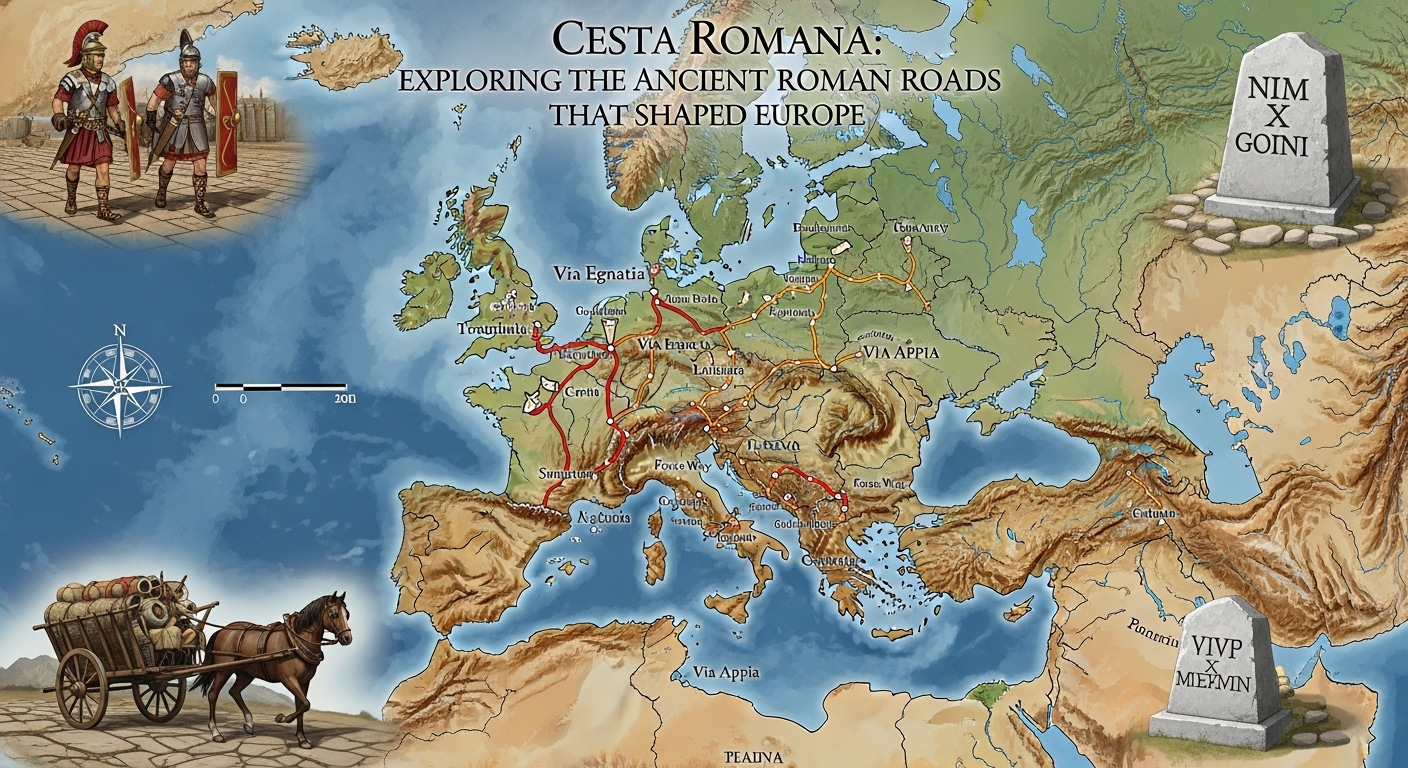
The term Cesta Romana (Latin: Via Romana) refers to the legendary network of Roman roads that connected the vast territories of the Roman Empire. These roads were more than simple travel routes — they were engineering marvels that enabled trade, military movement, communication, and cultural exchange across Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia.
Even today, many modern highways follow the paths originally laid by Roman engineers over 2,000 years ago.
What Does “Cesta Romana” Mean?
“Cesta Romana” translates to “Roman Road.” These were carefully designed stone-paved roads built during the time of the Roman Republic and later expanded under the Roman Empire.
The Romans constructed over 400,000 kilometers (250,000 miles) of roads, with around 80,000 kilometers paved with stone — an extraordinary achievement for ancient engineering.
Why Were Roman Roads Built?
Roman roads served several strategic purposes:
1. Military Efficiency
The Roman army could move quickly across provinces to defend or expand territory.
2. Trade and Commerce
Merchants transported goods such as olive oil, wine, metals, and textiles across continents.
3. Administration and Communication
Official messengers used the roads to deliver government documents and maintain control over distant regions.
4. Cultural Integration
Roads helped spread Roman language, laws, architecture, and traditions.
Famous Roman Roads (Cesta Romana Examples)
🛣️ Via Appia
🛣️ Via Egnatia
Stretching across the Balkans, this road connected the Adriatic Sea to Byzantium (modern-day Istanbul), playing a key role in East-West trade.
🛣️ Via Augusta
How Were Roman Roads Built?
Roman engineers followed a systematic construction method:
-
Excavation – A trench was dug for the road foundation.
-
Foundation Layer (Statumen) – Large stones formed a stable base.
-
Middle Layer (Rudus) – Gravel and crushed stones were added.
-
Top Layer (Summum Crusta) – Carefully fitted paving stones created a smooth surface.
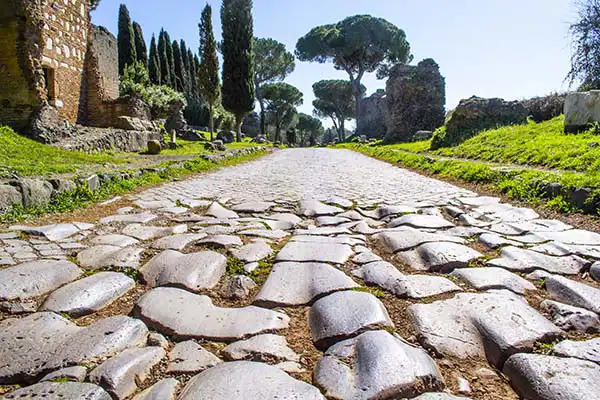
The roads were slightly curved in the center to allow rainwater drainage — a technique still used today.
Engineering Features of Cesta Romana
Roman roads included several innovative features:
-
Milestones marking distances
-
Drainage systems
-
Roadside inns (mansiones)
-
Bridges and tunnels
-
Straight-line planning across terrain
Their durability explains why many sections remain visible today.
Cultural and Historical Impact
The Roman road network unified the empire and accelerated economic development. It helped Latin evolve into modern Romance languages such as Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, and French.
In many European countries, modern highways still trace the original Roman routes.
Can You Visit Roman Roads Today?
Yes! Many sections of ancient Roman roads are preserved and open to tourists, especially in:
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
France
-
Croatia
-
Greece
-
Turkey
Walking on a Cesta Romana today offers a direct connection to ancient history.
Why Cesta Romana Still Matters
Roman roads represent:
-
Advanced ancient engineering
-
Strategic military innovation
-
Cultural connectivity
-
Infrastructure longevity
They laid the groundwork for modern transportation networks across Europe.
Final Thoughts
Cesta Romana symbolizes the brilliance of Roman engineering and organization. These roads were the arteries of one of history’s greatest empires, shaping commerce, culture, and communication for centuries.
Even after two millennia, their legacy continues to influence the structure of modern cities and highways.
FAQs About Cesta Romana
Q1: How long did Roman roads last?
Many have survived for over 2,000 years due to durable construction methods.
Q2: Who built Roman roads?
Primarily Roman soldiers and specialized engineers.
Q3: Are Roman roads still used today?
Some have been incorporated into modern roads, while others remain historical landmarks.